A MPI example http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/ParallelComputing/cfiles/send-recv7.c program using broadcast and non-blocking receive;
- Consists of one sender process and up to 7 receiver processes.
- The sender process sends a message containing its identifier to all the other processes. These receive the message and replies with a message containing their own identifier.
- Both processes use non-blocking send and receive operations (MPI_Isend and MPI_Irecv, and MPI_Waitall).
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mpi.h"
#define MAXPROC 8 /* Max number of processes */
main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int i, x, np, me;
int tag = 42;
MPI_Status status[MAXPROC];
/* Request objects for non-blocking send and receive */
MPI_Request send_req[MAXPROC], recv_req[MAXPROC];
int y[MAXPROC]; /* Array to receive values in */
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv); /* Initialize */
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &np); /* Get nr of processes */
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &me); /* Get own identifier */
x = me; /* This is the value we send, the process id */
if (me == 0) { /* Process 0 does this */
/* First check that we have at least 2 and at most MAXPROC processes */
if (np<2 || np>MAXPROC) {
printf("You have to use at lest 2 and at most %d processes\n", MAXPROC);
MPI_Finalize();
exit(0);
}
printf("Process %d sending to all other processes\n",me);
/* Send a message containing the process id to all other processes */
for (i=1; i<np; i++) {
MPI_Isend(&x, 1, MPI_INT, i, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &send_req[i]);
}
/* While the messages are delivered, we could do computations here */
/* Wait until all messages have been sent */
/* Note that we use requests and statuses starting from position 1 */
MPI_Waitall(np-1, &send_req[1], &status[1]);
printf("Process %d receiving from all other processes\n", me);
/* Receive a message from all other processes */
for (i=1; i<np; i++) {
MPI_Irecv (&y[i], 1, MPI_INT, i, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &recv_req[i]);
}
/* While the messages are delivered, we could do computations here */
/* Wait until all messages have been received */
/* Requests and statuses start from position 1 */
MPI_Waitall(np-1, &recv_req[1], &status[1]);
/* Print out one line for each message we received */
for (i=1; i<np; i++) {
printf("Process %d received message from process %d\n", me, y[i]);
}
printf("Process %d ready\n", me);
} else { /* all other processes do this */
/* Check sanity of the user */
if (np<2 || np>MAXPROC) {
MPI_Finalize();
exit(0);
}
MPI_Irecv (&y, 1, MPI_INT, 0, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &recv_req[0]);
MPI_Wait(&recv_req[0], &status[0]);
MPI_Isend (&x, 1, MPI_INT, 0, tag, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &send_req[0]);
/* Lots of computations here */
MPI_Wait(&send_req[0], &status[0]);
}
MPI_Finalize();
exit(0);
}
- Use MPI_Wtime to benchmark the performance.
- Rewrite the code such that both processes use blocking send and receive operations (MPI_send and MPI_recv). Use MPI_Wtime to compare the performance change.
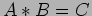 , each element in the result matrix
, each element in the result matrix 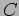 is formed by taking a row of
is formed by taking a row of 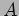 and a column of
and a column of 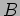 , multiplying each element of the row with the corresponding element of the column (these must be the same length), and summing these values. Sequential implementation;
, multiplying each element of the row with the corresponding element of the column (these must be the same length), and summing these values. Sequential implementation;
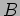 (and
(and 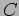 ), NRA is the number of rows in
), NRA is the number of rows in 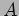 (and
(and 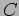 ), and NCA is the number of columns in
), and NCA is the number of columns in 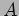 (and rows in
(and rows in 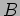 ).
).
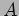 , and replicating matrix
, and replicating matrix 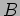 on all tasks. Each task generates one or more rows of the result matrix
on all tasks. Each task generates one or more rows of the result matrix 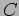 . Looking at the C code fragment above, the work is distributed according to the "i" index.
. Looking at the C code fragment above, the work is distributed according to the "i" index.
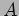 has to be multiplied against all columns of
has to be multiplied against all columns of 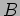 , all data passed to each task is used by that task.
, all data passed to each task is used by that task.
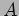 on all tasks, and distributing columns of matrix
on all tasks, and distributing columns of matrix 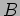 to each task. Each task generates one or more columns of the result matrix. Looking at the Fortran code fragment, the work is distributed according to the "k" index.
to each task. Each task generates one or more columns of the result matrix. Looking at the Fortran code fragment, the work is distributed according to the "k" index.