



Next: Multiple Bus Systems
Up: Bus-based Dynamic Interconnection Networks
Previous: Bus-based Dynamic Interconnection Networks
Contents
Single Bus Systems
Figure 2.1:
Single Bus System.
|
|
- A single bus is considered the simplest way to connect multiprocessor systems. Figure 2.1 shows an illustration of a single bus system.
- In its general form, such a system consists of N processors, each having its own cache, connected by a shared bus.
- The typical size of such a system varies between 2 and 50 processors. The actual size is determined by the traffic per processor and the bus bandwidth (defined as the maximum rate at which the bus can propagate data once transmission has started).
- The single bus network complexity, measured in terms of the number of buses used, is
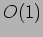 , while the time complexity, measured in terms of the amount of input to output delay is
, while the time complexity, measured in terms of the amount of input to output delay is 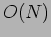 .
.
- Although simple and easy to expand, single bus multiprocessors are inherently limited by the bandwidth of the bus and the fact that only one processor can access the bus, and in turn only one memory access can take place at any given time.




Next: Multiple Bus Systems
Up: Bus-based Dynamic Interconnection Networks
Previous: Bus-based Dynamic Interconnection Networks
Contents
Cem Ozdogan
2006-12-27
![\includegraphics[scale=0.6]{figures/singlebus.ps}](img42.png)