- Since the amount of disk space is limited (posing a management problem similar to that of physical memory), it is necessary to reuse the space released by deleted files
- In general, file systems keep a list of free disk blocks (initially, all the blocks are free) and manage this list by one of the following techniques
- Bit tables (see Fig. 6.18b)
- Individual bits in a bit vector flags used/free blocks
- 16GB disk with 1KB blocks; for each block 1 bit is used
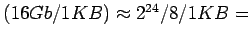 2048 blocks; 2MB table
2048 blocks; 2MB table
- 16GB disk with 512byte blocks 4MB table
- May be too large to hold in main memory
- Expensive to search; But may use a two level table
- Chained free portions (see Fig. 6.18a)
- Free portions are linked
- Fragmentation if using variable allocation
 many small portions
many small portions
- Required read before write to a block
- Free block list
- Single list of a set of free block lists (unallocated blocks)
- Manage as LIFO or FIFO on disk with ends in main memory
- Background jobs can reorder list for better contiguity
Figure 6.18:
(a) Storing the free list on a linked list (b) A bit map.
|
|
2004-05-25