



Next: Cluster Examples
Up: Myrinet Clos Network
Previous: Myrinet Clos Network
Contents
The Quadrics Network
Figure 10.8:
Quaternary fat tree of dimension 1 (left) and Elite switch of Quadrics networks (right).
|
|
- The Quadrics network (QsNet) consists of two hardware building blocks: a programmable network interface called Elan and a high-bandwidth, low-latency communication switch called Elite.
- The Elan network interface connects the Quadrics network to a processing node containing one or more CPUs. In addition to generating and accepting packets to and from the network, Elan provides substantial local processing power to implement high-level
message passing protocols such as the Message Passing Interface (MPI).
- QsNet connects Elite switches in a quaternary fat-tree topology. A quaternary fat
tree of dimension
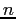 is composed of
is composed of  processing nodes and
processing nodes and
 switches interconnected as a delta network. It can be recursively built by connecting four quaternary
fat trees of dimension
switches interconnected as a delta network. It can be recursively built by connecting four quaternary
fat trees of dimension  . Figure 10.8left and -right shows quaternary fat trees of dimensions 1 and 2, respectively. When
. Figure 10.8left and -right shows quaternary fat trees of dimensions 1 and 2, respectively. When  , the network consists of one switch and four processing nodes. When
, the network consists of one switch and four processing nodes. When  , the network consists of eight switches and 16 processing nodes.
, the network consists of eight switches and 16 processing nodes.
- Elite networks are source routed. The Elan network interface attaches route information
to the packet header before transmitting the packet into the network.
- The route information is a sequence of Elite link tags. As the packet moves inside the network, each switch removes the first route tag from the header and forwards the packet to the next switch in the route or the final destination.
- Packets are routed using wormhole routing flow control (each packet is divided into flow control digits (flits)). In QsNet, the size of each flit is 16 bits. Network nodes can send packets to multiple destinations using the network's broadcast capability.




Next: Cluster Examples
Up: Myrinet Clos Network
Previous: Myrinet Clos Network
Contents
Cem Ozdogan
2006-12-25