



Next: Introduction
Up: Ceng 505 Parallel Computing
Previous: List of Tables
Contents
- View of the Field and Abstraction Layers
- MIMD Shared Memory, MIMD Distributed Memory, SIMD Distributed Computers, and Clusters.
- Interconnection Network Taxonomy and Four Decades of Computing.
- SISD, SIMD, amd MIMD Architectures.
- Two SIMD Schemes.
- Two MIMD Categories; Shared Memory and Message Passing MIMD Architectures.
- Bus Based and Switch Based Shared Memory INs, Single Bus Based and Multiple Bus Based Shared Memory INs.
- Examples of Static Topologies.
- Single-Stage, Multi-Stage and Crossbar Switch Dynamics INs.
- Performance Comparisons of Some Dynamics INs and Performance Characteristics of Static INs.
- Cooperative-Communicating with other processes.
- One sided-Communicating with other processes.
- Single Bus System.
- Multiple bus with full bus memory connection (MBFBMC); multiple bus with single bus-memory connection (MBSBMC); multiple bus with partial bus memory connection (MBPBMC); and multiple bus with class-based memory connection (MBCBMC).
- An
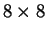 crossbar network (a) straight switch setting; and (b) diagonal switch setting.
crossbar network (a) straight switch setting; and (b) diagonal switch setting.
- The different settings of the
 SE.
SE.
- Multistage interconnection network and an example
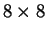 Shuffle-Exchange network (SEN).
Shuffle-Exchange network (SEN).
- Multistage interconnection network and an example
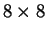 Shuffle-Exchange network (SEN).
Shuffle-Exchange network (SEN).
- Completely Connected Network.
- A 4-cube.
- A
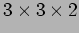 mesh network.
mesh network.
- Performance Comparison of Dynamic Networks.
- Performance Characteristics of Static Networks.
- MPI messages.
- Data+Envelope.
- MPI basic datatypes for C.
- left-top; Correct Execution of Library Calls, right-top; Incorrect Execution of Library Calls, left-bottom; Correct Execution of Library Calls with Pending Communcication, right-bottom; Incorrect Execution of Library Calls with Pending Communication.
- Example program segments.
- Power-cost relationship according to Grosch's law.
- The Possible Speedup and Efficiency for Different
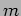 and
and 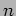 .
.
- Shared memory systems.
- Shared memory via two ports.
- Bus-based UMA (SMP) shared memory system.
- NUMA shared memory system.
- COMA shared memory system.
- Write-Through vs. Write-Back.
- Write-Update vs. Write-Invalidate.
- Supervisor-workers model used in most parallel applications on shared memory systems.
- Serial process vs. parallel process and two parallel processes communicate using the shared data segment.
- Locks and barriers.
- A sample OpenMP program along with its Pthreads translation that might be performed by an OpenMP compiler.
- Message passing systems.
- An example of a message passing system.
- Hypercube broadcast tree-based communication.
- Communication latencies in the store-and-forward (SF) and wormhole (WH) techniques.
- Comparison Among a Number of Switching Techniques.
- Typical SP 3 node.
- Handshake for a blocking non-buffered send/receive operation.
- Blocking buffered transfer protocols: (a) in the presence of communication hardware with buffers at send and receive ends; and (b) in the absence of communication hardware, sender interrupts receiver and deposits data in buffer at receiver end.
- Space of possible protocols for send and receive operations.
- Non-blocking non-buffered send and receive operations (a) in absence of communication hardware; (b) in presence of communication hardware.
- Performance of Send/Receive on a Number of Message Passing Machines.
- Using MPI_Comm_split to split a group of processes in a communicator into subgroups.
- Representation of network technologies.
- A multithreaded server in a client server system.
- A socket connection.
- Supervisor workers model in client server.
- A cluster made of homogenous single-processor computers.
- Source-path routing vs. table-based routing.
- A 128-host Clos network using 16-port Myrinet switch (upper) and
a 64-host Clos network using 16-port Myrinet switch (each line represents
two links).
- Quaternary fat tree of dimension 1 (left) and Elite switch of Quadrics networks (right).
Cem Ozdogan
2006-12-27