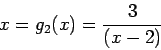Iteration algorithm with the form 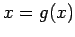

The method may converge to a root different from the expected one, or it may diverge. Different rearrangements will converge at different rates.
Figure 3:
The fixed point of 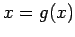 is the intersection of the line
is the intersection of the line 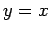 and the curve
and the curve 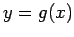 plotted against x.
plotted against x.
|
2004-10-18